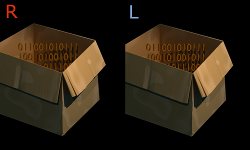
Stereoscopic pair consist of two slightly different images of the same size captured from for left and right eyes (e.g. from two camera positions). This pair can be stored in various ways in the file:
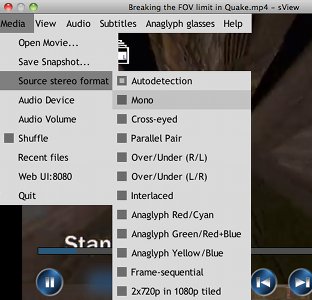
- Mono - no stereoscopic information, only single view is provided
- Dual Stream - each view is stored in independent stream or file
- Cross-eyed, Parallel pair - two images packed horizontally, also known as Side-by-Side
- Over/Under - two images packed vertically, also known as Top-Bottom
- Interlaced - row interleaved (obsolete)
- Anaglyph - image stored for glasses with color filters (obsolete)
- Frame-sequential - views (frames) interleaved in time (first frame Left view, second frame Right view and so on)
- 2x720p in 1080p tiled - special layout used by some TV broadcasters in Europe
Program will be able to show image properly only when stereoscopic format has been properly selected. sView is able to determine stereoscopic format using:
- Multiple streams (*.mpo, *.mkv, *.wmv). Two image / video streams of the same size are automatically detected as stereoscopic pair with Left view in the first stream.
- JPEG image containing
JPSmarker (VRex extension). JPS marker defines stereoscopic format. - PNG image containing
sTERchunk (Extensions to the PNG). Only parallel pair with views order can be defined by sTER indicator. - WMV metadata (*.wmv).
The following metadata fields will be interpreted by sView:
StereoscopicLayoutdefining one of layouts (SideBySideRF,SideBySideLF,OverUnderLT,OverUnderRT)StereoscopicHalfHeightandStereoscopicHalfWidthdefining anamorphic videoStereoscopicHorizontalParallaxdefining parallax in pixels
- MKV metadata (*.mkv, *mkv3d).
Matroska specification includes dedicated fields defining stereoscopic layout (
StereoMode). FFmpeg library converts this data in form of stream metadata with nameSTEREO_MODE(with valuesmono,right_left,left_right,bottom_top,top_bottom,row_interleaved_rl,row_interleaved_lr,block_lr,block_rl,anaglyph_cyan_red,anaglyph_green_magenta). Note that detection code in sView is generalized and specified metadata tags will be read from any video file (not only *.mkv). - h264 SEI messages (per frame side data, *.mp4, *.mkv). Some codecs stores stereoscopic identification data at every frame. This technically allows to switch from mono to stereo3d within the same stream. FFmpeg provides this information in form of AVStereo3D structure - thus sView will be able to read this information for all decoders in FFmpeg supporting this feature.
- File extension (*.pns, *.jps). Image files with extensions *.pns (PNG file) and *.jps (JPEG file) will be interpreted as stereoscopic pair in Side-by-side format with Right view first (cross-eyed).
- File name.
sView supports the following name convention for stereoscopic format identification:
half-ou,-hou,-abqdefine anamorphic Over/Under pairhalf-sbs,-hsbs,-lrq,-rlqdefine anamorphic Side-by-side pair-ba,-abdefine Over/Under pair-sbs,-lr,-rldefine Side-by-side pair
Anamorphic stereo pair with Side-by-side and Over/Under layout is a special format introduced for compatibility with build-in TV players and existing hardware players without HDMI 1.4a+ support. Video stored in this format has broken pixel proportions - it identifies itself as normal 16:9 video with 1080p HD resolution (1920x1080). Both are important - old hardware players have been unable to decode videos of greater side, and 16:9 proportions allow transferring video image through HDMI without extra scaling or cropping which should be normally applied. So in general this format has been created as a temporary hack entrenched for much longer time than expected…
Normally files should contain appropriate stereoscopic metadata to be properly displayed by players without user involvement. Unfortunately, many files still created without this information requiring manual configuration by user.
If your file has been opened wrong you should try to change “source stereo format”. In most cases this is just layout which defines how left and right views are stored in single frame. At first step you should select “Mono” format to see the original frame.